Your Cart is Empty



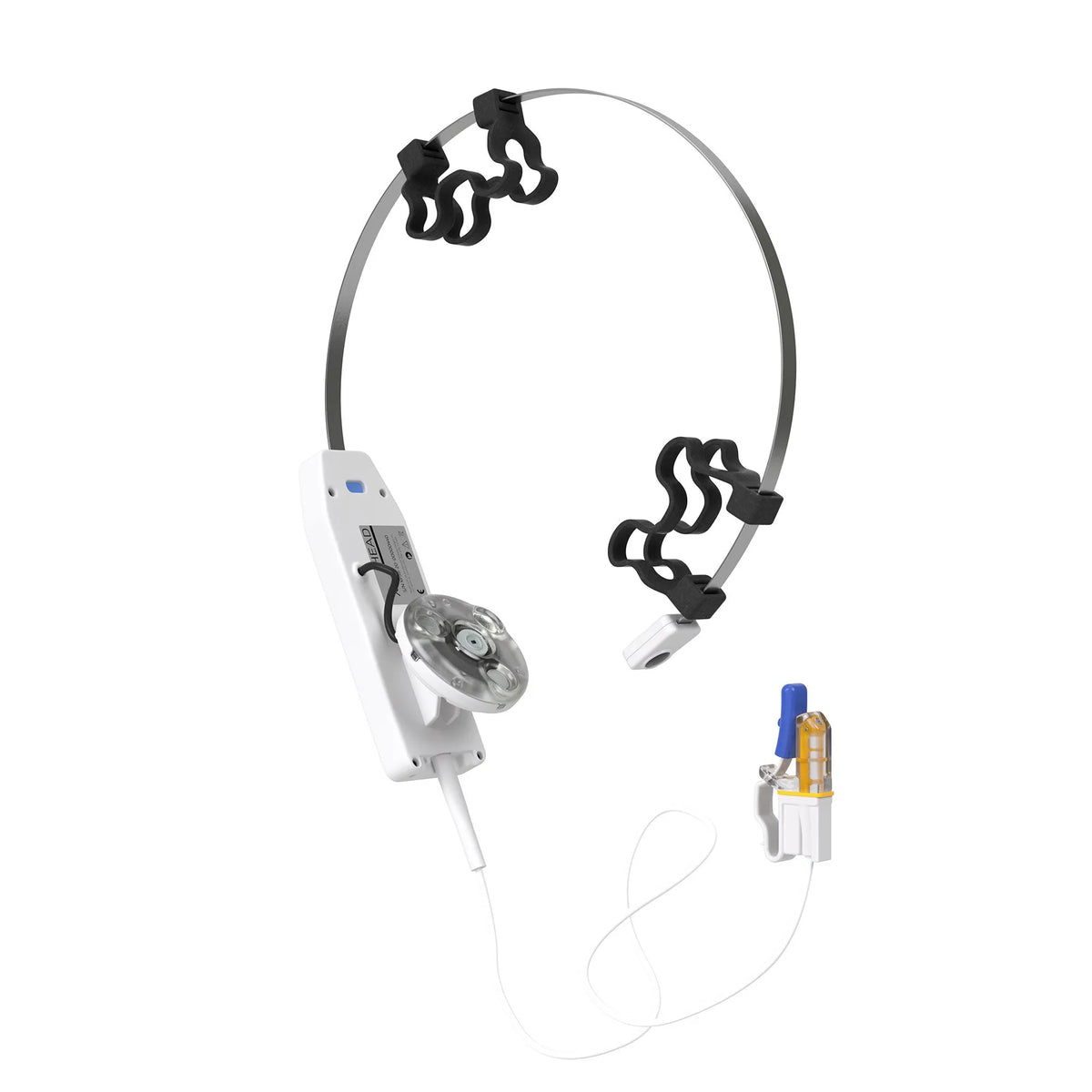
Vielight X-Plus 4 Brain Photobiomodulation Device
$449.00$0.00
- ✓ Questions? Call: 351 200 4050
- ✓ Sleep Recharged is a trusted Dealer
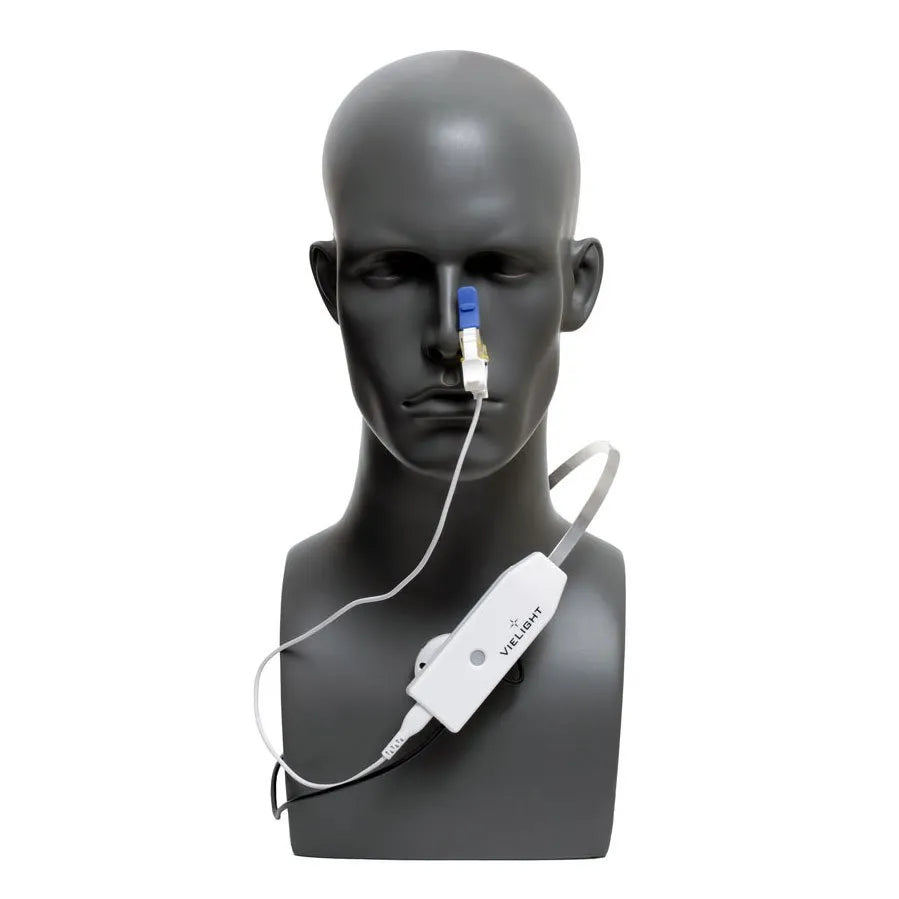
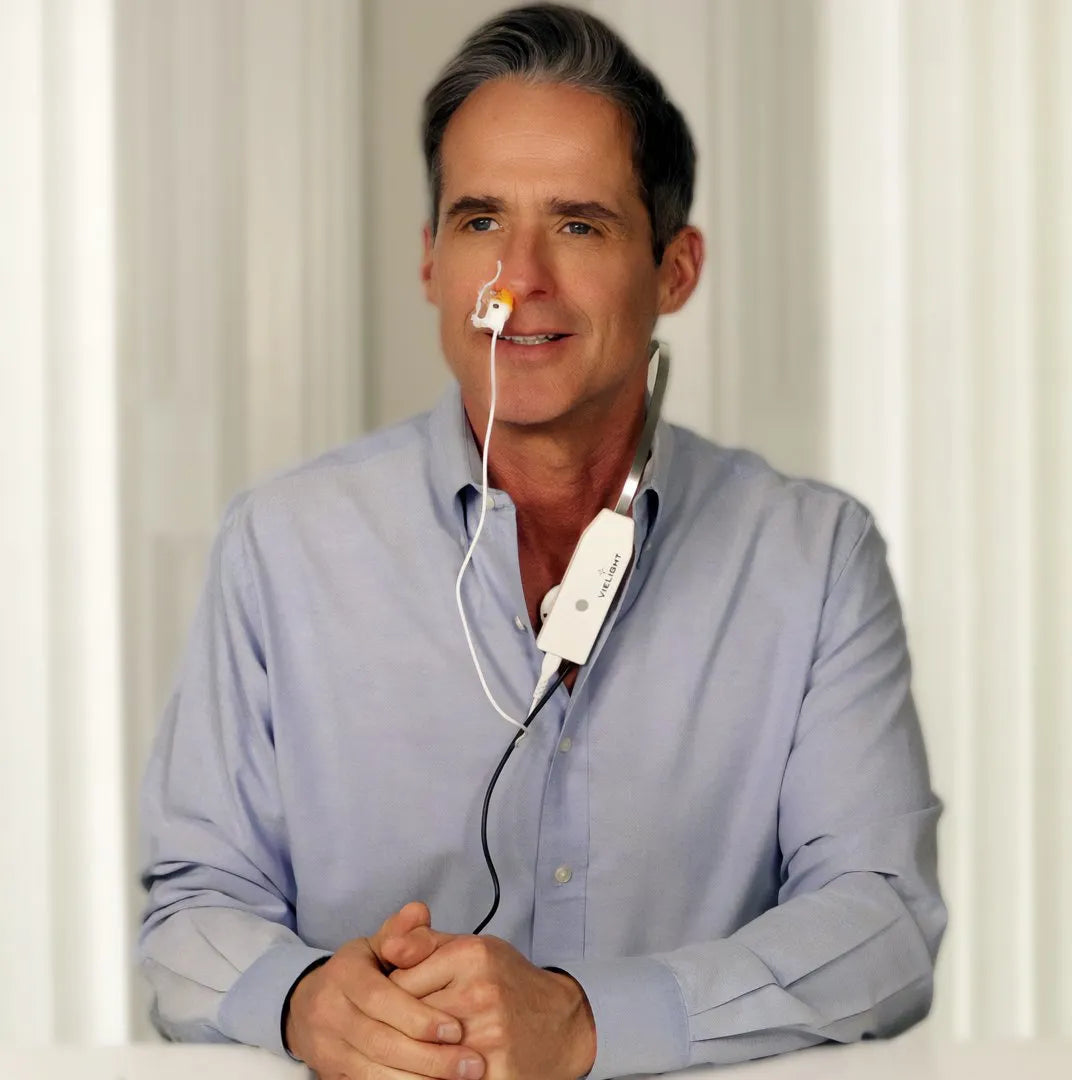
X-Plus 4 Brain Photobiomodulation Device
The Vielight X-Plus stimulates the thymus gland and nasal vasculature with light energy to augment the body’s innate immune system and reduces inflammation.
The Vielight RX-Plus produced statistically significant results in an n=295 clinical trial for Covid-19 recovery and received Health Canada approval.
| Target structure | Benefit |
|---|---|
|
Improved immunity. |
|
Improved immunity and systemic fitness. |
Specifications
| Power Density | Irradiance |
50 mW/cm² (1) : Body Module LED |
|---|---|
| LED Power |
1000 mW per module |
| Targeted Areas |
Cerebellum, Occipital lobe, Thymus gland, Nasal vasculature |
| Head Size Suitability |
Minimum age: 5 years old |
| Medical Grade Certification |
ISO13485 and MDSAP |
| Safety Certification |
TÜV Rheinland |
| Warranty |
24 months |
| Satisfaction Guarantee |
We have an 80% refund policy, valid for 3 months from the time of purchase |
Warranty: One-year manufacturer’s warranty.
Shipping: We have shipping depots located in California (United States), Ontario (Canada) and Perth (Australia). We ship internationally to Europe. Shipping times may vary between 2-14 business days.
Returns: Your Vielight product purchases are backed by a 6-months no-question-asked return policy which entitles you to receive 80% of your purchase price back within the first 6 months from the date of the purchase.
Important Note: Our customer support, satisfaction guarantee and product warranty will not apply to devices sold through unauthorized channels, such as Amazon and eBay.
More Info: Please note that this product comes with an intranasal applicator.
Health Canada Approval
Vielight Inc. Receives Health Canada Approval for Treatment of Covid-19 with Near Infrared Device Technology
Approval from Canada’s Top Federal Health Agency Followed Positive Clinical Trial Results

We are honored to announce that the Vielight RX Plus device has received medical device approval from Health Canada!
We conducted an n=295 clinical trial for Covid-19 recovery for which the results were statistically significant.
This represents two historic milestones:
- The RX Plus is the first medical device to be approved for the treatment of COVID-19 infection.
- The RX Plus is the first non-invasive photobiomodulation (PBM) technology to be approved for a major indication.
The RX Plus combines our patented red and near-infrared light technology to accelerate the recovery of adults with COVID-19. We designed it to be non-invasive, portable, and lightweight to meet the needs of those who prefer to recover at home or on-the-go.
- Clinical trial results can be found here: https://medrxiv.org/cgi/content/short/2022.06.16.22276503v1
- Information on the Health Canada license can be found here: https://health-products.canada.ca/mdall-limh/information?companyId=136815&lang=eng
- In the past, we worked with Harvard Medical School on anti-pathogenic research using blue light energy: https://www.vielight.com/research/#anti-viral
The effects of Photobiomodulation on Immunity.
(The text below is based on an article from Liebert A, Bicknell B, Markman W, Kiat H. A Potential Role for Photobiomodulation Therapy in Disease Treatment and Prevention in the Era of COVID-19. Aging Dis. 2020 Dec 1;11(6):1352-1362. doi: 10.14336/AD.2020.0901. PMID: 33269093; PMCID: PMC7673843)
PBM appears to exert pluripotent effects in the modulation of inflammation and immunity [1]. Many studies have demonstrated that PBM modulates inflammation by reducing the pro-inflammatory cytokines (such as IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α) and other inflammatory markers released from activated inflammatory cells, while increasing the anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10) [2]. The immuno-modulatory effect of PBM on cytokines regulation and the complement cascade occurs via the POMC pathway, involving regulation of the hypothalamic pituitary axis through the direct modulation of the POMC/melanocortin signalling pathway including a-MSH, a potent anti-inflammatory molecule. The POMC pathway is regulated by PBM [3], which in turn modulates both ACTH and β-opioid, as well as, interestingly, ACE activity [4].
One of the central effects of PBM on the immune response is via the modulation of neutrophil function [5] by balancing neutrophil numbers, improving neutrophil efficiency and modulating the neutrophil extracellular trap formation [6]. Reducing over-accumulation of neutrophils is a major mechanism for the effect of PBM in reducing acute lung inflammation [7]. This is crucial in preventing the cytokine storm cascade in autoimmune diseases. PBM also modulates the ratio of M1 and M2 macrophage phenotypes, reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines and increasing anti-inflammatory cytokines and thus balance the inflammatory process [8].
These inflammatory changes facilitated by PBM have profound effects on many body processes. For example, PBM therapy has been shown to modulate peripheral blood mononuclear cells and CD4+ cells to reduce inflammatory effects in multiple sclerosis patients and healthy adults by increasing IL-10 and reducing IFN-γ [9, 10]. PBM reduces the number of inflammatory cells, pro-inflammatory cytokines as well as fibrotic tissue in a mouse model of lung fibrosis [11]. Acute lung inflammation in rats is reduced with PBM to reduce oedema, neutrophil influx and TNF-α, while reducing IL-10 in rats [12].
In an experimental model of induced acute peritonitis in rats, Yu and co-workers [13] showed PBM resulted in lymphocyte proliferation and enhanced lymphocyte ATP synthesis compared to controls, and the 60-day survival rate of the PBM group was double that of the control group (p<0.001). Assis et al [14] further demonstrated the immune modulation capability of PBM, with septic rats treated with PBM exhibiting lower IL-6 activity and decreased atrogin-1 and MuRF-1 immuno-expression (markers of sepsis related muscle catabolic states).
PBM causes mitogenic stimulation responsive lymphocyte proliferation and enhanced lymphocyte ATP synthesis [15]. A plausible mechanism for PBM induced lymphocytic proliferation is through the reaction of light with haemoglobin, resulting in oxygen radical production [16]. Indeed, in immunological cells, PBM induces production of reactive oxygen species, NO or interleukins most often, leading to an anti-inflammatory effect [17]. It is well documented that various immune response processes are highly dependent on cellular energy, the latter being depressed in sepsis and septic shock cases [18, 19]. The mitochondria probably act as photo-acceptors for PBM and robustly reactivate cellular energy synthesis to re-establish ATP levels in a variety of cells including lymphocytes and macrophages, and through several pathways that trigger activation of nucleic acid synthesis and cellular proliferation [20, 21].
Reference
- Liebert A, Bicknell B, Markman W, Kiat H. A Potential Role for Photobiomodulation Therapy in Disease Treatment and Prevention in the Era of COVID-19. Aging Dis. 2020 Dec 1;11(6):1352-1362. doi: 10.14336/AD.2020.0901. PMID: 33269093; PMCID: PMC7673843.
Clinical Research
| Condition | Topic | Institution | Vielight Device | Research Type | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
University of California San Francisco | US Veterans Affairs | Vielight Neuro Gamma | Clinical Study | Completed |
|
Harvard Medical School | Boston University School of Medicine | Vielight Neuro Gamma | Clinical Study | Completed |
|
Unity Health, Toronto | Vielight Neuro Gamma | Clinical Study | Analysis Stage |
|
University of Florida | University of Arizona | National Institute on Aging | Vielight 810 [MIP] | Phase 2 Clinical Trial (n=168) | Ongoing |
|
St Michael’s Hospital | Vielight Inc | Vielight Neuro Gamma | Phase 3 Clinical Trial (n=228) |
Ongoing |
|
University of California San Francisco | US Veterans Affairs | Vielight Neuro Gamma | Clinical Study | Results Analysis |
|
Department of Neurology, University of Utah | Vielight Neuro Gamma | Clinical Trial (n=49) | Pre-publication |
|
Boston University School of Medicine | Harvard Medical School | Vielight Neuro Gamma | Clinical Study | Completed |
|
VA Advanced Imaging Research Center, San Francisco VA Health Care System | Vielight Neuro Gamma | Clinical Study | Completed |
|
Boston Veterans Affairs Research Institute | Vielight Neuro Gamma | Clinical Study | Ongoing |
|
University of Sydney | Vielight Neuro Gamma | Clinical Study | Completed |
|
University of Florida | Vielight 810 [MIP] | Phase 2 Clinical trial (n=135) | Ongoing |
|
University of Sydney | University of Brisbane | Vielight Neuro Gamma | Clinical Study | Registered |
|
University of California San Francisco | US Veterans Affairs | Vielight Neuro Alpha | Clinical Study | Completed |
|
Neurodevelopment Division, Istituto di Neuroscienze, Italy | Vielight Neuro Duo | Clinical Study | Completed |
|
Vielight Inc | Vielight RX Plus | Pivotal Phase 3 Clinical Trial (n=295) | Completed |
|
University of Toronto | Vielight Inc | Vielight Neuro Gamma | Clinical Study | Completed |
|
Vielight Inc | Vielight Neuro Alpha | Clinical Study | Pre- Publication |
|
Princeton University | University of Alberta | Vielight Inc | Vielight Neuro Alpha | Research Study | Completed |
|
Vielight Inc | Vielight RX Plus | Pivotal Phase 3 Clinical Trial (n=295) | Completed |
|
Harvard Medical School | Vielight Blue [MIP] | Scientific Study | Completed |
|
Harvard Medical School | Vielight Blue [MIP] | Scientific Study | Completed |
|
Harvard Medical School | Vielight Blue [MIP] | Scientific Study | Completed |
|
University of Deusto, Spain | University of Montpellier, France | Pennsylvania State University | Vielight Neuro Gamma | Clinical Research (n=56) | Completed |
|
University of Alberta | Polytechnic University of Turin | Vielight Neuro Alpha | Scientific Study | Completed |
- Alzheimer’s Disease (Dementia)
Effects of Home Photobiomodulation Treatments on Cognitive and Behavioral Function and Resting-State Functional Connectivity in Patients with Dementia: A Pilot Trial
Institutes – University of California San Francisco & the Veterans Affairs USA
[ Published Study Device: Vielight Neuro Gamma ]
Significant Improvement in Cognition in Mild to Moderately Severe Dementia Cases Treated with Transcranial Plus Intranasal Photobiomodulation: Case Series Report
Co-authoring institutes – Harvard Medical School, Boston University School of Medicine
[ Published Study | Device: Vielight Neuro Gamma ]
Vielight Neuro RX Gamma – Alzheimer’s Disease Pivotal Phase III Clinical Trial (n=228)
Co-institutes – St Michael’s Hospital, Toronto
[ Clinical Trial Information Link ] (228 participants | 3 years | Ongoing)
Neuro RX Gamma for Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment (aMCI) / Dementia
Co-institutes – Unity Health Toronto, Toronto
[ Clinical Trial Information Link | Device: Vielight Neuro Gamma ]
Revitalizing Cognition in Older Adults at Risk for Alzheimer’s Disease With Near-Infrared Photobiomodulation
Institutes – University of Florida, University of Arizona, National Institute on Aging (NIA)
[ Clinical Trial Information Link | Device: Vielight Neuro Gamma ] (168 participants | 5 years | Registration)
Impact of Photobiomodulation (PBM) on Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease
Institutes – University of California San Francisco UCSF
[ Clinical Trial Information Link / Device: Vielight Neuro Gamma ] (16 participants | 1.5 years | Ongoing)
- Traumatic Brain Injury / Concussion
Transcranial Photobiomodulation Treatment Effects In Former Athletes With Repetitive Head Hits (n=49)
Institutes – Department of Neurology, University of Utah
[ Published Abstract Link | Device: Vielight Neuro Gamma ] (49 participants | Pending publication)
Transcranial Photobiomodulation Treatment: Significant Improvements in Four Ex-Football Players with Possible Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy
Institutes – Boston University School of Medicine, Harvard Medical School
[ Published Study Link | Device: Vielight Neuro Gamma ]
Changes in Brain Function and Structure After Self-Administered Home Photobiomodulation Treatment in a Concussion Case
Institutes – VA Advanced Imaging Research Center, San Francisco VA Health Care System, Departments of Radiology & Biomedical Imaging and Psychiatry & Behavioral Sciences, University of California, San Francisco
[ Published Study Link | Device: Vielight Neuro Gamma ]
Photobiomodulation to Improve Cognition in TBI, With fMRI
Institutes – Boston Veterans Affairs Research Institute
[ Clinical Trial Information Link | Device: Vielight Neuro Gamma ] (20 participants | 1 years | Ongoing)
- Parkinson’s Disease
Improvements in clinical signs of Parkinson’s disease using photobiomodulation: A prospective proof-of-concept study
Institutes – University of Sydney, University of New South Wales, Griffith University
[ Published Study Link Device: Vielight Neuro Gamma ]
Pilot Intervention With Near Infrared Stimulation
Institutes – University of Florida
[ Clinical Trial Information Link | Device: Vielight Neuro Gamma ] (135 participants | 4 years | Ongoing)
Evaluation of dose of Photobiomodulation (Light) Therapy and Physiotherapy for Improving Quality of Life Outcomes and Mobility in Parkinson’s Disease (Pilot)
Institutes – University of Sydney, University of Brisbane
[ Clinical Trial Information Link | Device: Vielight Neuro Gamma ] (16 participants | 1.5 years | Ongoing)
- PTSD and Gulf War Illness
Improvements in Gulf War Illness Symptoms After Near-Infrared Transcranial and Intranasal Photobiomodulation: Two Case Reports
Institutes – University of California San Francisco & the Veterans Affairs USA
[ Published Study Link | Device: Vielight Neuro Alpha ]
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Transcranial Photobiomodulation for the Treatment of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): A Retrospective Study
Institutes – Neurodevelopment Division, Istituto di Neuroscienze, Italy, Department of Psychiatry, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, NY
[ Published Study Link Device: Vielight Neuro Duo ]
- Covid-19
Vielight RX Plus for the Treatment of COVID-19 Respiratory Symptoms
Various clinical sites
[ Pre-print of Results ] (295 participants | 1 year | Pre-publication)
- Post-Covid
A Pilot Study Evaluating the Efficacy of the Vielight Neuro RX Gamma in the Treatment of Post COVID-19 Cognitive Impairment
Various clinical sites
[ Clinical Trial Information ] (36 participants | 1 year | Recruitment)
- Cognitive Enhancement and EEG-Neuromodulation
Enhancement of Divergent Creative Thinking After Transcranial Near-Infrared Photobiomodulation Over the Default Mode Network
Institutes – University of Deusto | University of Montpellier | Pennsylvania State University
[ Published Study Link Device: Vielight Neuro Gamma ]
Pulsed Near Infrared Transcranial and Intranasal Photobiomodulation Significantly Modulates Neural Oscillations: a pilot exploratory study
Institutes – Centre for Therapeutic Brain Intervention, Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
[ Published Study Link (Nature, Scientific Reports, 2019) | Device: Vielight Neuro Gamma ]
Modulation of cortical oscillations using 10hz near-infrared transcranial and intranasal photobiomodulation: a randomized sham-controlled crossover study
[ Abstract Text Link | Device: Vielight Neuro Alpha ]
- Bioenergetics and Cellular Enhancement
Near-Infrared Photobiomodulation of Living Cells, Tubulin, and Microtubules In Vitro
Institutes – Department of Physics and the Department of Chemistry, University of Alberta | Scholes Lab, Department of Chemistry, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ, United States | Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Politecnico di Torino, Turin, Italy | Vielight Inc
[ Published Study Link | Device: Vielight Neuro Alpha ]
Raman Spectroscopy Reveals Photobiomodulation-Induced α-Helix to β-Sheet Transition in Tubulins: Potential Implications for Alzheimer’s and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases
Institutes – University of Alberta, Polytechnic University of Turin, Freie Universit¨at Berlin, Silesian University of Technology
[ Pre-print | Device: Vielight Neuro Alpha ]
Downloads
Video
You may also like
Contact form
Got a question or need assistance? We're here for you!
Thanks for visiting our website. We value your time and are always happy to help. Please fill out the contact form below with your name, email address, and message, and we'll get back to you as soon as possible.
We look forward to hearing from you and assisting with any questions or concerns you may have.